Metabolism is an important bodily function that converts food to energy to maintain regular body processes like breathing and digestion. As we age our metabolism can become slower.
A slow metabolism can lead to weight gain, hormone changes, decreased energy production, and overall health.
Fortunately, metabolism isn’t static. Factors like staying active, eating a balanced diet of protein-rich foods, staying hydrated, getting adequate sleep, and managing stress levels can help to increase metabolism.
Why Does Metabolism Decrease With Age?
As we age, maintaining a healthy metabolism becomes increasingly important. For those over 60, understanding and addressing the factors that influence metabolism can significantly enhance overall health and vitality.
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism is the motor that keeps our bodies functioning.
Metabolism refers to the chemical process in our bodies that converts food into energy.
The speed at which your body processes food is known as your metabolic rate. Your basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body requires at rest, without any physical activity, to maintain essential bodily functions.
Someone with a fast metabolism has a higher BMR compared to someone with a slow metabolism, meaning they typically burn more calories.
Metabolism is important as it plays a role in maintaining:
- Energy Production: Ensuring you have the energy to perform daily activities.
- Body Weight Management: Influencing how you gain or lose weight.
- Overall Health: Affecting everything from hormone balance to immune function.
As we age, several factors contribute to slower metabolism.
- Muscle Mass Decline: Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue. Aging often leads to muscle loss, reducing the body’s calorie-burning efficiency.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones that regulate metabolism, such as thyroid hormones, may decrease with age.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Older adults may be less active, further slowing down metabolic rates.
Tips to Help Increase Metabolism
While age can play a role in metabolic breakdown there are several ways to boost your metabolism and enhance your overall well-being even after age 60.
Metabolism isn’t static. Factors like exercise, diet, and chemistry all influence your metabolic rate. Incorporating an active lifestyle, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management can help increase your metabolism.
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is essential.
It’s recommended that older adults get at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity a week or 75 minutes of vigorous physical activity a week.
Moderate physical activity can include:
- Walking
- Biking
- Swimming
- Gardening
Vigorous physical activity may include:
- Running or jogging
- Lap swimming
- Fast or uphill biking
- Jumping rope
In addition to aerobic physical activity, older adults are encouraged to strengthen muscles at least twice a week using weights or resistance. This helps to maintain and build muscle and healthy joints. Activities can include:
- Barre
- Pilates
- Weight training
- Body weight exercises like pushups, squats, and glute bridges
Routine physical activity can help to increase metabolism and help prevent heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Eat Protein-Rich Foods
Protein requires more energy to digest compared to fats and carbohydrates, thereby increasing your metabolic rate.
Foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins like beans and lentils are great ways to incorporate more protein into your diet.
Eating smaller portions of food frequently throughout the day can help keep your metabolism active. Long periods of fasting can slow down your metabolism. Try to avoid fasting for long periods of time.
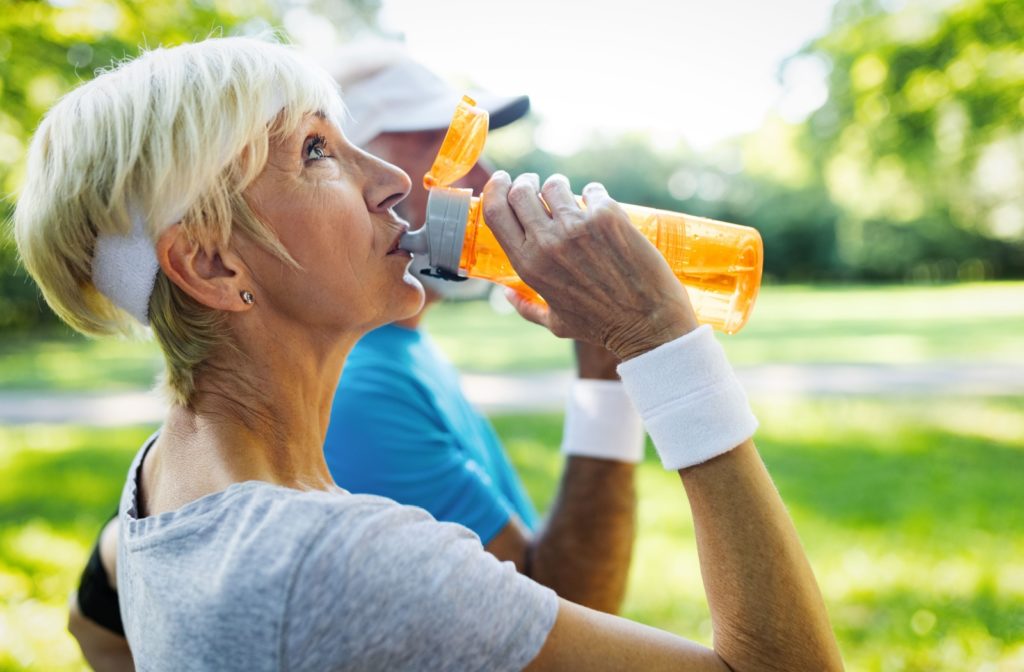

Stay Hydrated
Water is crucial for metabolic function. Drinking enough water can help ensure your metabolism runs smoothly. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
Get Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for metabolic health. Even during periods of rest, your metabolism is still active. Research suggests that a lack of sleep can impact one’s metabolic rate.
Poor sleep can disrupt hormone levels, increase blood glucose levels, and insulin resistance, and lead to weight gain.
Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of quality, uninterrupted sleep per night.
Manage Stress
Stress has many negative effects on the body due to increased cortisol levels and insulin resistance.
When the body experiences stress, it triggers several hormonal and biochemical responses that affect how energy is produced, stored, and used. Chronic stress can lead to decreased metabolic rates.
During periods of stress, some individuals may increase their craving for high-calorie, sugary, and fatty foods. Others may turn to emotional eating turning to foods that may lead to weight gain.
Managing stress levels can include arranging routine physical activity, maintaining social community, getting adequate levels of sleep, and practicing meditation or yoga.
Connect With our Team
Maintaining a balanced, active, and healthy lifestyle can help to increase metabolism. Staying connected with a community can help as well!
The Landmark of Fridley can provide a sense of community, helping to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Contact our team to schedule a tour to learn more about events and activities!